
15311826613
Click to add WeChatAlthough my country has a large reserve of iron ore, most of it is "poor, fine and impure", with large differences in mineral properties and great difficulty in beneficiation. At present, the process of beneficiation of hematite that can be processed includes stage grinding or continuous grinding, coarse and fine separation, gravity separation-high gradient magnetic separation-anion reverse flotation process, continuous grinding, strong magnetic separation-anion reverse flotation process and roasting, stage grinding-high efficiency magnetic separation-cation reverse flotation process. However, the specific selection depends on the properties of the hematite ore. Below we take a fine-grained hematite as an example to introduce one of the hematite beneficiation process flows.

Iron is the main optional element in the hematite, which contains magnetite, hematite, iron silicate, iron carbonate and iron sulfide, etc. The main gangue mineral is SiO2, and the harmful impurities phosphorus and sulfur are very low, which has little effect on the grade of iron concentrate.
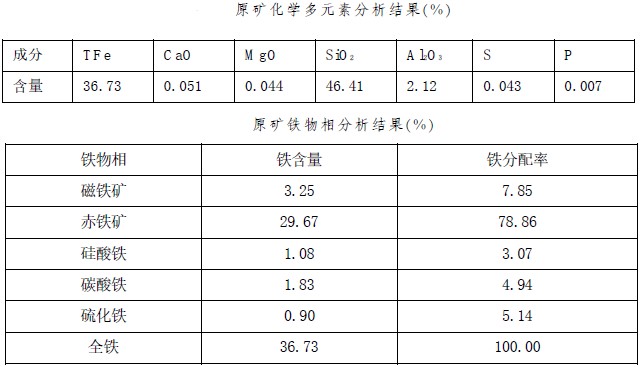
According to the statistics of the embedded particle size of iron minerals under a microscope, the monomer dissociation degree of iron minerals must reach more than 90%, and grinding to -0.043mm accounts for 90% to achieve mineral monomer dissociation. Therefore, in the ore dressing process, it is necessary to pay attention to the grinding and classification process, and give full play to the role of pre-strong magnetic tailing, so that while achieving a relatively sufficient monomer dissociation of the mineral, the mud caused by over-grinding can be reduced. The impact on subsequent sorting operations.
Finally, through the analysis of beneficiation experiments, a reasonable beneficiation process was designed for the fine-grained hematite ore: stage grinding-weak magnetic separation-high gradient strong magnetic separation-gravity separation-reverse flotation process. Among them, grinding fineness is -0.074mm accounting for 83%, feed concentration is 28%, weak magnetic field strength is 1200Oe, strong magnetic field strength is 10000Oe and 8000Oe respectively. Under this condition, the iron concentrate grade obtained can reach 65.32%, and the iron recovery rate is 80.43%.

The most prominent feature of this process is that after grinding, the minerals are magnetically separated and tailings are discarded, and then the minerals are subjected to strong magnetic separation, and a part of the tailings are discarded as soon as possible, which can improve the efficiency and beneficiation effect of subsequent operations; in addition, the tailings of the strong magnetic separation are separated by a shaking table, and the concentrate and the coarse concentrate obtained by magnetic separation are finely ground, which can fully dissociate the iron minerals, and finally remove the gangue minerals by reverse flotation to obtain a product with a higher iron concentrate grade.
The above is an introduction to the beneficiation process of a fine-grained hematite ore. In actual beneficiation plants, since the properties of the ore contained in each mineral are different, it is not possible to generalize. Therefore, it is recommended to conduct a beneficiation test first, and then design a suitable hematite beneficiation process plan through test analysis to achieve an ideal return on investment.