
15311826613
Click to add WeChatGold ore dressing occupies a pivotal position in the gold production system. With the continuous development of the global economy, the demand for gold continues to rise, and improving the efficiency of gold ore dressing and resource utilization has become the key to the sustainable development of the gold industry. This article deeply analyzes the process of gold ore dressing, and elaborates on the key links such as crushing and grinding, reverse flotation process, weak magnetic separation process, and flotation.
Crushing and grinding are the key pre-process of gold ore dressing. Its core goal is to fully separate gold minerals from gangue minerals and create favorable conditions for subsequent separation operations. Among many ore dressing plants in my country, the two-stage one-closed circuit crushing process is widely used. The process first uses coarse crushing equipment (such as jaw crusher) to initially crush large pieces of ore to reduce its particle size to a certain extent. Subsequently, it is further crushed by medium and fine crushing equipment (such as cone crusher), and the output ore particle size is more uniform. In the closed-loop link, screening equipment is used to screen the crushed products, and unqualified coarse products are returned to the crusher for re-crushing to ensure that the particle size of the final crushed product meets the requirements of subsequent grinding operations.
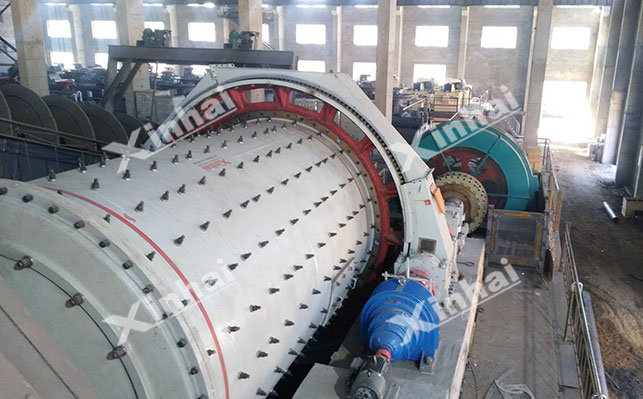
Grinding operations usually use ball mills, rod mills, etc. The principle is to grind the ore to a suitable fineness through the impact and grinding of steel balls on the ore. If the grinding is too coarse, the gold minerals and gangue minerals are not fully dissociated, which will lead to a decrease in the gold recovery rate; if the grinding is too fine, it will increase energy consumption and production costs, and may also cause over-crushing, affecting the subsequent operation effects such as flotation. Therefore, in actual production, it is necessary to accurately control the grinding fineness according to factors such as the properties of the ore and the particle size of the gold minerals.
Reverse flotation process is widely used in the beneficiation of fine-grained dispersed gold ores. For this type of ore, the gold minerals are fine in particle size and dispersed in the gangue minerals, and traditional beneficiation methods are difficult to achieve effective separation. The reverse flotation process is to add specific flotation agents to make the surface of the gangue minerals hydrophobic, so that they float out first, while the gold minerals remain in the slurry to achieve the purpose of separation. For example, for gold mines containing a large amount of gangue minerals such as quartz, inhibitors can be added to inhibit gold minerals, and then collectors can be used to float the gangue minerals.

The significant advantage of the reverse flotation process is that it can obtain high-quality concentrates. By accurately controlling the type and amount of flotation agents, impurities in the ore can be effectively removed and the grade of gold concentrate can be improved. However, this process also has limitations. It has high requirements for ore properties, and the selection and use of flotation agents are relatively complicated. It needs to be determined by experiments based on the specific composition and properties of the ore, which increases the complexity and cost of the process.
In order to overcome the limitations of a single beneficiation method, reverse flotation is often combined with other beneficiation methods in actual production. For example, for some complex gold mines, gravity separation can be used to pre-discard some gangue minerals to reduce the processing volume of subsequent operations, and then reverse flotation can be carried out to improve the gold recovery rate and concentrate grade. Reverse flotation can also be used in combination with weak magnetic separation. Magnetic minerals are first removed by weak magnetic separation to reduce their interference with reverse flotation, and then reverse flotation is carried out to further improve the separation effect.
The advantages of this combined process are obvious. On the one hand, the beneficiation process can be flexibly adjusted according to the properties of the ore, giving full play to the advantages of different beneficiation methods and improving resource utilization; on the other hand, it can save economic resources, reduce unnecessary equipment investment and reagent consumption, and at the same time improve work efficiency and reduce production costs.

Flotation is one of the most widely used methods in gold ore beneficiation. Flotation columns play an important role in reverse flotation of non-ferrous metals and gold desulfurization. The working principle of the flotation column is to use air to generate tiny bubbles in the ore pulp. The gold minerals attach to the bubbles and float to the surface of the ore pulp. After forming a foam layer, they are scraped out to achieve separation from the gangue minerals.
Compared with traditional flotation machines, flotation columns have many advantages. It can simplify the process, reduce the number of equipment and floor space, and reduce investment costs. The flotation column has high sorting accuracy, which can effectively improve the purity of the ore and significantly improve the grade of the gold concentrate. In the gold mine desulfurization reverse flotation, the flotation column can efficiently remove sulfur and other impurities in the ore and improve the quality of the gold concentrate.
The gold ore dressing process is a complex and critical system engineering. Crushing and grinding, reverse flotation process, weak magnetic separation process, flotation and other links are interrelated and affect each other. In actual production, the ore dressing process should be scientifically and reasonably selected and combined according to the nature, grade, embedded particle size and other factors of the gold ore, and the advantages of each process should be fully utilized to improve the ore dressing efficiency and resource utilization.