
15311826613
Click to add WeChatAt present, with the depletion of high-grade gold reserves, the research on medium- and low-grade, difficult-to-process gold ores and the strengthening of traditional gold beneficiation technology have become the mainstream trend of global gold selection. Gold ore has a high mining value, its beneficiation process is relatively complex, and the beneficiation methods are even more different. At present, the common gold beneficiation processes mainly include cyanidation, flotation and gravity separation.

Next, we will first explain the cyanidation gold selection process.
Cyanidation is one of the main methods for gold beneficiation. Generally, cyanidation can be divided into two categories: stirring cyanidation and percolation cyanidation. Among them, stirring cyanidation is mainly used to treat flotation gold concentrate or full mud cyanidation; while percolation cyanidation is mainly used to treat low-grade gold-containing oxidized ores. At the same time, in response to the disadvantages of using sodium cyanide and the current environmental protection requirements, researchers have successfully developed a non-toxic gold leaching agent to replace sodium cyanide for cyanidation gold extraction. The method of use is the same as that of sodium cyanide, but its recovery is faster, the leaching rate is higher, and the cost is lower.
The stirring cyanidation gold extraction process mainly includes two types of gold extraction process flows. One is the so-called cyanidation-zinc replacement process (CCD method and CCF method) that recovers gold by continuous countercurrent washing and replacement precipitation with zinc powder (silk); the other is the non-filtration cyanidation carbon slurry process (CIP method and CIL method) that does not require filtration and washing, and uses activated carbon to directly adsorb and recover gold from cyanide slurry.
The cyanide-zinc replacement process (CCD method and CCF method) is used to treat the precious gold solution after cyanide leaching. The principle is to use zinc powder (silk) as a reducing agent to replace gold and silver from the leachate. It mainly includes countercurrent washing solid-liquid separation, leachate purification, deoxidation, and zinc powder (silk) replacement operations.
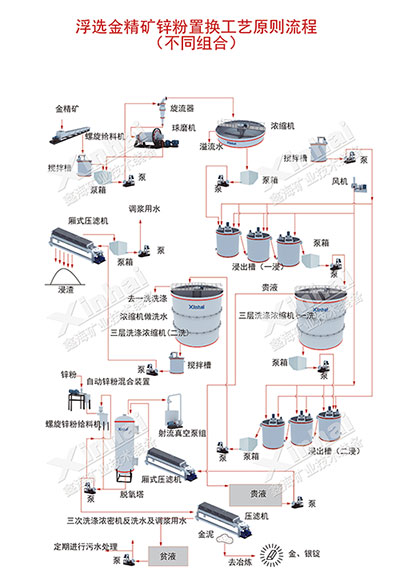
Countercurrent washing solid-liquid separation: Separate the precious liquid (leachate) after cyanidation from the solid.
Leachate purification:Remove suspended matter from the precious liquid (leaching liquid) to make the gold-containing precious liquid entering the replacement operation clear and transparent.
Deoxidation:Remove dissolved oxygen from the precious liquid (leaching liquid).
Zinc powder (silk) replacement:Use zinc powder (silk) to replace the precious metals in the precious liquid (leaching liquid) to form gold (silver) mud.
The carbon-in-pulp gold extraction process (CIP method and CIL method) is to put activated carbon into cyanide slurry, adsorb the dissolved gold on the activated carbon, and then extract gold from the activated carbon. It mainly includes leaching raw material preparation, stirring leaching and countercurrent carbon adsorption, gold-loaded carbon desorption, electrolytic electrolysis, smelting ingots, carbon regeneration and other operations.
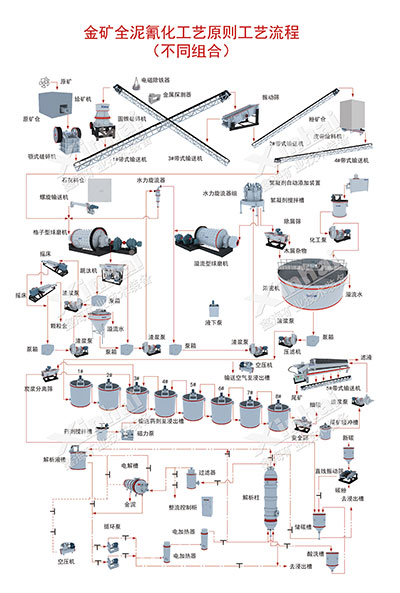
Preparation of leaching raw materials
When carbon leaching gold extraction process is adopted, the preparation of leaching raw materials includes physical crushing and grinding classification. Usually, the overflow fineness of grinding classification in carbon leaching gold extraction process is mostly -200 mesh accounting for 85-95%.
Debris removal
Wood chips and debris in the slurry are easy to cause pipes and screens to be blocked, and are also easy to absorb gold in the slurry and mix it into the rich carbon, so they must be removed before leaching. If necessary, pulp concentration and descaling agent should be added. Descaling agent can also reduce the scaling on the surface of activated carbon and sieve. Generally, two chip removal operations are required in the grinding process, one at the overflow of the first and second grinding and classification. The chip removal equipment mostly uses medium-frequency linear vibrating screen. In the first chip removal operation, spiral screen and drum screen can also be used. The screen size of the chip removal screen should be as small as possible while ensuring that the screen surface does not run.
Pre-leaching concentration operation
When the overflow concentration of grinding and classification is mostly 18-22%, it is not suitable for direct leaching and the pulp must be thickened. It is recommended to use a high-efficiency concentrator with small footprint and high concentration efficiency.

Stirring leaching and countercurrent carbon adsorption
In the gold mine CIP process, leaching and adsorption are two independent operations. In the adsorption operation, the leaching process has been basically completed, and the size, number and operating conditions of the adsorption tank are determined by the adsorption parameters. In the gold mine CIL process, leaching and adsorption operations are carried out simultaneously. Generally speaking, the leaching operation takes longer than the adsorption operation, so the size of the tank, aeration and dosing are determined by the leaching parameters. Since the adsorption rate is a function of the concentration of dissolved gold in the solution, in order to increase the concentration of dissolved gold in the front adsorption tank and increase the leaching time, 1-2 levels of pre-leaching are usually added before leaching and adsorption.

Desorption and electrolytic electrolysis of gold-loaded carbon
The gold-loaded carbon and slurry are sent to the carbon separation screen (generally a linear vibrating screen) through a carbon pump or air lift, and washed with clean water on the screen to separate the carbon from the slurry. The gold-loaded carbon enters the carbon storage tank, and the slurry and washing water enter the first stage adsorption tank. At present, the commonly used desorption method of gold-loaded carbon is the high-temperature and high-pressure desorption method, that is, anions that are easily adsorbed by activated carbon are added to the desorption system to replace Au(CN)2- to achieve gold desorption; the precious liquid obtained by desorbing the gold-loaded carbon is recovered by ionization to obtain solid gold.

Smelting and ingot making
After pickling and impurity removal, the gold mud can be directly smelted into gold ingots. Using hydrometallurgy, the purity of gold ingots can reach more than 99.99%.
Carbon regeneration
After adsorption and desorption, activated carbon needs to be regenerated to restore its good adsorption performance. Generally, the activated carbon after desorption is first acid-washed to remove carbonates and other accumulations. After several returns, it needs to be thermally activated to restore the adsorption activity of the carbon, and then it can be recycled. The main equipment includes activated carbon regeneration kiln, water quenching tank, fine carbon separation screen, etc.
The ion exchange resin adsorption method is basically similar to the carbon slurry leaching and adsorption process. The difference is that the carbon is replaced by ion exchange resin, including gold-loaded resin analysis electrolysis, smelting ingot making, resin regeneration and other operations.
Gold-loaded resin analysis electrolysis
The gold-loaded resin and slurry are pumped to the resin separation screen (generally a linear vibrating screen) by a pump or air lifter, and rinsed with clean water on the screen to completely separate the resin from the slurry. The gold-loaded resin enters the resin storage tank, and the slurry and rinsing water enter the first stage adsorption tank.
The cleaned gold-loaded resin is fed into the analysis column, and the analysis liquid is added. The cycle operation is carried out for 36 hours at a temperature of 40-60°C. The analyzed precious liquid enters the electrolytic cell and the gold mud is recovered by ionization.
Smelting and ingot making
After pickling and impurity removal, the gold mud can be directly smelted into gold ingots. Using hydrometallurgy, the purity of gold ingots can reach more than 99.99%.

Resin Regeneration
The resin after analysis needs to be regenerated to restore its good adsorption performance. Add sodium hydroxide solution, stir intermittently and soak for 12 hours, drain the soaking liquid, wash with clean water until neutral and then recycle.
In addition, for some gold-bearing ores with complex ore properties, methods such as ore roasting + full mud cyanidation; bacterial leaching + full mud cyanidation can be used.