
15311826613
Click to add WeChatThe gold-loaded carbon electrolysis process is the main process in the cyanide gold extraction process. Whether it is the carbon leaching method or the carbon slurry method, the process uses activated carbon to adsorb gold (gold will be absorbed into the pores of activated carbon). At this time, the activated carbon that adsorbs gold is called gold-loaded carbon. Then the process of using the gold-loaded carbon to extract gold through electrolysis is the gold-loaded carbon electrolysis process.

Gold-loaded carbon and slurry are sent to the carbon separation screen (generally a linear vibrating screen) through a carbon pump or air lifter, and washed with clean water on the screen to separate the carbon from the slurry. The gold-loaded carbon enters the carbon storage tank, and the slurry and washing water enter the first adsorption tank. At present, the commonly used desorption methods of gold-loaded carbon include high temperature and high pressure desorption method, normal pressure heating desorption electrolysis method, heating and pressure desorption electrolysis method and alcohol desorption electrolysis method.

High temperature and high pressure desorption method: Add anions that are easily adsorbed by activated carbon to the desorption system to replace Au(CN)2- to achieve gold desorption; the precious liquid obtained by desorbing gold-loaded carbon is recovered by ionization to obtain solid gold.
Normal pressure heating desorption electrolysis method: At a temperature of 80-95℃ and normal pressure (1 atmosphere), NaCN and NaOH are used as desorption agents, and the electrolysis time is 50-70h. The normal pressure heating method has a long electrolysis time, low production capacity (low desorption rate and electrolysis rate) and high production cost.
Heating and pressurized desorption electrolysis method: At a temperature of 105-130℃ and a pressure of 0.15-0.3MPa, NaCH and NaOH are used as desorption agents, the desorption time is 30-48h, the desorption rate can reach 85-98%, and the electrolysis rate is ≥98%. However, this method is the same as the normal pressure heating method, with low efficiency, long time and high cost.
Alcohol (alcohol) desorption electrolysis method: At a temperature of 80-85℃ and normal pressure, 15-20% alcohol and NaOH, NaCH are used as desorption agents, and the electrolysis time is 12h. The main disadvantage of this process is that alcohol is volatile and flammable, which is not conducive to safe production, and the production capacity is small and the production cost is high.
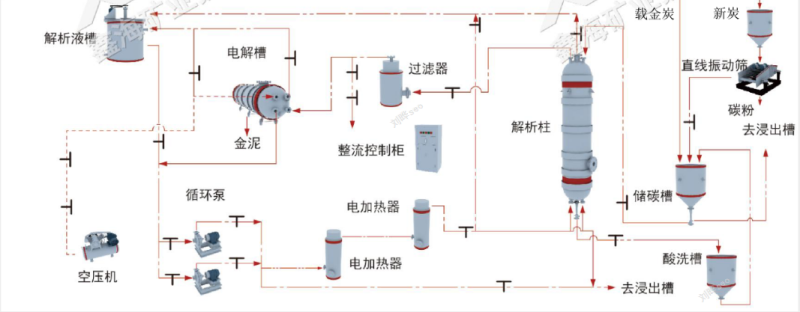
First, crush the gold ore into fine particles, which can be completed by crushing or grinding, because the crushed gold ore particles are more likely to contact with the electrolyte (the electrolyte is a solution containing gold ions), which improves its separation efficiency. This step can also be called gold pretreatment.
The pretreated gold particles are directly fed into the vibrating screen for screening, and the screened material enters the carbon storage tank. The carbon storage tank is set at the upper end of the desorption column. After the connecting valve is opened, it is added to the desorption column. Mineral particles with smaller particle size or not suitable for desorption process are screened and collected.
After the gold particles are fed into the desorption tank, desorption liquid (water and sodium hydroxide) is added. After the proportion is made according to the scale of gold-loaded carbon, the liquid reaches about 30-40 cm from the top of the liquid surface, and then the liquid flows into the circulation pump by gravity, and is fed into the heater through the pump for heating to 150°C. After the temperature is heated, the liquid reaches the bottom of the desorption tank, enters from the bottom and mixes with the gold-loaded carbon, floats through the carbon layer, and overflows from the overflow pipe. The overflowed liquid is fed into the filter to filter out impurities and mud, and then fed into the electrolytic cell for electrolysis. During the process, when the liquid in the electrolytic cell is full, the desorption tank valve is automatically closed and no more liquid is injected. The overflow in the electrolytic cell enters the circulation pump again, and the whole process needs to circulate for 6-8 hours.
When the temperature drops to about 110℃, the electrolytic cell starts to be powered on to reduce the gold mud. After this process, the carbon can be released. At this time, the carbon is no longer gold-loaded carbon and will return to the adsorption process to continue working. What is deposited in the electrolytic cell is gold mud.
The precipitated metallic gold is taken out of the electrolytic cell, and after subsequent treatment and refining, pure gold is finally obtained. These treatment and refining steps may include dissolution, filtration, precipitation, smelting, etc.
The gold-loaded carbon electrolysis process has high separation efficiency for gold; it is an environmentally friendly gold mining method with low reagent usage and low environmental pollution; it can also recover other useful metals in gold, such as silver and copper.

The above is an introduction to the gold-loaded carbon electrolysis process and flow. Although this method is an important means of obtaining gold, the actual ore dressing plant still needs to determine the appropriate process flow according to the properties of the gold ore. In addition to gold-loaded carbon gold extraction, there are also flotation gold extraction and gravity gold extraction processes. How to choose specifically requires first conducting ore dressing test analysis, and then designing a suitable gold extraction process. At the same time, a complete set of gold ore dressing equipment can be configured according to the process plan.