
15311826613
Click to add WeChatThe higher the purity of quartz sand, the wider its application field. In addition to the glass industry, it is also involved in high-tech industries. However, for high-tech industries, the purity of quartz sand is very high, and the SiO2 content must reach more than 99.99%. Iron (goethite, hematite, limonite, ilmenite, pyrrhotite, tourmaline, amphibole, biotite, etc.) is the main impurity of quartz sand. Currently, the commonly used methods for removing iron from quartz sand include mechanical scrubbing, magnetic separation, ultrasonic, flotation, acid leaching, etc. These methods can effectively remove iron-containing impurities, but have no obvious effect on the removal of titanium-containing iron impurities.
This article will introduce a new high-purity quartz sand to remove titanium iron process: the calcination-acid leaching titanium iron removal method, the process is: grinding, calcination, quenching, filtering, acid leaching, washing, drying, and finally obtaining high-purity quartz sand.
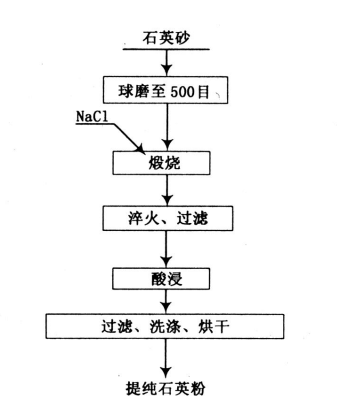
The grinding stage adopts a closed-circuit grinding. After the raw ore is crushed, it is fed into a grid ball mill for grinding. The grinding particle size requirement is 500 mesh. The grinding product is fed into the spiral classifier, and the overflow returns to the ball mill for re-grinding, and the bottom flow enters the next stage.

When calcining high-purity quartz sand, NaCl additives must be used to effectively remove iron and titanium impurities. The mechanism is that because quartz sand contains trace amounts of iron ores and titanium ores such as siderite (FeCO3) and limonite (Fe2O3), they will all be converted into Fe2O3 and TiO2 when roasted at high temperatures. NaCl decomposes Cl2 at high temperature, reacts with iron ore and titanium ore in quartz, generates gaseous FeCl3 and TiCl4 and is removed.
During calcination, the quartz sand raw material is placed in a high-purity corundum crucible, and the crucible is placed in a resistance furnace for calcination. The calcination conditions are 2% NaCl addition, calcination temperature 820℃, and calcination time 2h.
Quenching and filtration is to quickly cool the quartz sand particles in cold water after calcination to remove bubbles, water marks and some impurities inside the mineral. When quartz sand is calcined at high temperature, it will undergo a crystal transformation (α quartz → β quartz → β tridymite), which will increase its volume and make the original defects in the crystal more serious. After quenching, the crystal volume suddenly decreases, and the internal stress at the defects of the crystal increases rapidly, causing the crystal to break at the defects, and then filter to remove impurities.
The acid leaching process can be hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid method, but the effect of using either alone is not ideal, but after adding hydrofluoric acid to form a mixed acid, the iron removal effect is more obvious, especially after mixing with hydrofluoric acid, it can not only promote the dissolution of iron ore in quartz sand, but also has a complexing effect on dissolved iron ions; at the same time, hydrofluoric acid can react with quartz, exposing the iron impurities wrapped in quartz to the surface, and the newly generated particles have high surface activity, which is conducive to the reaction of iron oxides with acid and promotes their dissolution. The acid leaching conditions are 18% hydrochloric acid + 2% hydrofluoric acid, and the acid leaching temperature is 50℃.
Washing and drying of high-purity quartz sand is the final step. The quartz sand is washed by a spiral sand washer, and high-purity quartz sand is dried. The mineral is fed into the drying cylinder by a belt conveyor for drying.
The above is the treatment method for high-purity quartz sand with high ferro-titanium content. In actual ore dressing plants, it is more complicated to remove ferro-titanium from high-purity quartz sand. Conventional process methods often cannot obtain ideal purity. Therefore, it is recommended to conduct ore dressing test, remove impurities in a targeted manner, and obtain high-purity quartz sand ore.