
15311826613
Click to add WeChatTungsten resources are mostly obtained from wolframite, scheelite and mixed black and white tungsten ores. However, due to long-term development, easy-to-select tungsten and rich tungsten ores have been almost exhausted, but my country's demand for tungsten resources has only increased. Therefore, only associated tungsten deposits or difficult-to-select tungsten deposits can be developed to obtain tungsten resources.
Tungsten associated with other metal mines in my country accounts for more than 20% of tungsten reserves, and is generally recovered comprehensively with the development of the main mineral resources. Let's learn how to select these tungsten deposits>.

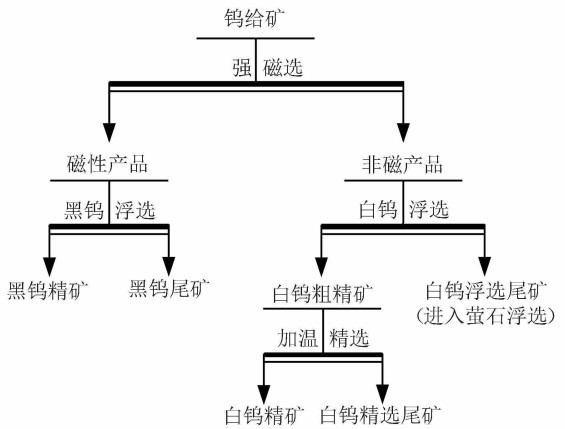
A complex low-grade black and white tungsten paragenetic ore, through ore dressing test research has designed a process flow of strong magnetic diversion-separation of black and white tungsten, namely "black and white tungsten mineral diversion and speed-differentiation asynchronous ore dressing", which is characterized in that after the flotation of the sulfide ore, a pulsating high-gradient strong magnetic machine is used to divert and select the black tungsten rough concentrate, and then it is selected by flotation to obtain the black crane concentrate; the magnetic tailings are used to obtain the scheelite rough concentrate by flotation, and the scheelite concentrate is obtained by heating and selection. The new process replaces the original operation of mixed flotation and separation of black and scheelite minerals, eliminates the inhibition of wolframite flotation, greatly improves the recovery rate of black and white crane minerals, and is beneficial to the subsequent flotation recovery of smelter and cassiterite. The industrial test obtained a white crane concentrate grade of 65.52% and a recovery rate of 38.51%, a black tungsten concentrate WO3 grade of 33.58% and a recovery rate of 38.01%, and a total tungsten recovery rate of 1.5%. 76.52%, compared with the index before the adoption of this process, the tungsten recovery rate increased by 14%. The recovery rate of fluorite concentrate increased from less than 30% before the industrial test to 40%.
The traditional scheelite concentration method "Petrov method" is to add a large amount of water glass to the scheelite rough concentrate, heat and stir at high concentration, and then dilute and remove the drug for many times before flotation of white crane. This method has a good effect on the concentration of scheelite rough concentrate with relatively high grade and simple mineral composition.

However, it is difficult to work on scheelite rough concentrate with low tungsten grade and high content of calcium gangue minerals and sulfide minerals. Some calcium gangue minerals such as fluorite and calcite that are easy to float are difficult to suppress, or scheelite minerals are also excessively suppressed and lost in the selected tailings. Therefore, new mineral processing technology can be used for selection, such as the collector-enhanced re-adsorption-tri-alkali selective desorption and drug removal direct selection method, that is, before the selection of scheelite rough concentrate, the collector is added to strengthen the re-adsorption of the collector by tungsten minerals, and then water glass, sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide are added to utilize the difference in the adsorption and desorption ability of tungsten minerals and calcium-containing non-target minerals to enhance the selective desorption, drug removal and inhibition of calcium-containing non-target minerals, while the floating of scheelite is basically unaffected. After heating or stirring at room temperature, the slurry is directly floated without dilution, desludging or drug removal, which greatly simplifies the selection operation, avoids the loss of scheelite during multiple dilutions, and further improves the grade and recovery rate of tungsten concentrate.
In molybdenum-tungsten isomorphous scheelite (Ca[(W, Mo)O4]), the MoO3 content is 1%~10%, and the MoO3 content of some molybdenum-rich scheelite is as high as 34%, which weakens the floatability of scheelite. For this type of difficult-to-select tungsten ore, TA-3 and high-efficiency combined collectors can be used to complete flotation. For example, a 1500t/d molybdenum ore dressing plant used this method to select tungsten, and the final generation index was stable, and the final tungsten concentrate grade reached more than 60%.

In addition to the above-mentioned new tungsten beneficiation methods, there are also some combined processes such as normal temperature flotation-scheelite heating concentration-weak magnetic separation-strong magnetic separation-shaking table gravity separation process, cyclone concentration-normal temperature flotation-centrifuge concentration process, centrifuge pretreatment-flotation-gravity separation, desulfurization-centrifuge-flotation-magnetic separation, etc., which can be used for beneficiation of difficult-to-select tungsten ores, but how to choose The tungsten beneficiation process must ultimately be determined based on the properties of the tungsten ore.