
15311826613
Click to add WeChatGravity separation is a physical separation method that uses the density difference of mineral particles in the gravity field to separate. In the process of gold extraction from carbonaceous gold ore, the gravity separation process separates gold minerals and carbonaceous materials according to the density difference between gold minerals and carbonaceous minerals (such as organic carbon, graphite, etc.), thereby improving the recovery rate of gold minerals. Since the density of carbonaceous minerals is usually low and the density of gold minerals is high, the gravity separation process is particularly effective for some carbonaceous gold ores.
Common gravity separation technologies for carbonaceous gold ore include shaking table gravity separation, jig gravity separation, chute gravity separation and centrifugal gravity separation, each of which has its own characteristics and scope of application.

The shaking table is a widely used gravity separation equipment with an inclined bed surface, which is driven by a transmission device to perform reciprocating asymmetric motion. After the slurry is fed into the shaking table, under the combined action of water flushing and bed surface vibration, minerals of different densities move in different directions and speeds. Gold particles with high density move to the concentrate end and transmission end of the bed surface, while gangue minerals with low density are washed to the tailing end by water flow. For example, in a carbonaceous gold mine, the symbiotic relationship between gold and carbonaceous materials is complex. The shaking table gravity separation method can effectively separate gold and carbonaceous materials under the conditions of feed concentration of 20%-30%, stroke of 16-20mm, and stroke of 250-300 times/min, and obtain high-grade gold concentrate with a gold recovery rate of 70%-80%. The shaking table gravity separation method has a good separation effect on fine-grained gold, and can effectively separate gold from carbonaceous materials and gangue minerals with large density differences, and obtain high-grade gold concentrate. However, the processing capacity is relatively small, the floor space is large, and the equipment and operation requirements are high.

The jig machine uses periodic up and down alternating water flow to stratify the ore particles according to density in the jigging chamber. The rising water flow loosens the ore particle group, and the ore particles with low density rise quickly and are in the upper layer; the gold particles with high density rise slowly and are in the lower layer. When the water flows downward, the gold particles in the lower layer are more likely to settle to the bottom, and the heavy products (containing gold concentrates) are discharged through the ore discharge device to separate gold from other minerals. When processing a carbonaceous gold ore, the gold particle size of the ore is between 0.5-2mm. The jigging gravity separation method is used. Under the conditions of a water flow frequency of 30-40 times/min and a water flow amplitude of 30-50mm, the gold recovery rate can reach 60%-70%. The jigging gravity separation method has a large processing capacity, good recovery effect on coarse gold, relatively simple equipment structure, and convenient operation and maintenance. However, the recovery effect on fine gold is poor, the separation accuracy is limited, and it is difficult to obtain high-grade gold concentrate.
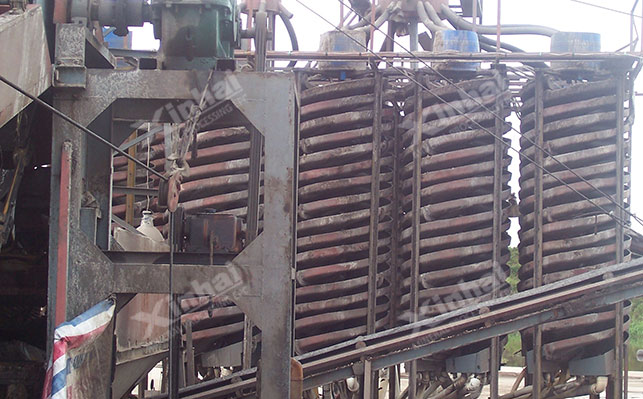
The chute is an inclined trough with grooves or rough linings on the surface. The slurry flows along the chute under the action of gravity. The gold particles with high density are precipitated and enriched at the grooves or rough surfaces under the combined action of friction, water flow resistance and gravity, and the gangue minerals with low density are discharged with the water flow. For some sandy carbonaceous gold mines, the chute gravity separation method can be used to effectively recover the gold in the chute under the conditions of a chute slope of 5°-10° and a slurry flow rate of 0.1-0.3m/s. The chute gravity separation method has simple equipment, low cost, good recovery effect on coarse gold, and can be easily operated in the field. However, it occupies a large area, has a relatively low recovery rate, and has a poor recovery effect on fine gold, which is greatly affected by the properties of the ore and operating conditions.

Centrifugal gravity separation equipment uses the centrifugal force field generated by high-speed rotation to subject the mineral particles in the slurry to a centrifugal force much greater than gravity. The gold particles with high density quickly move to the inner wall of the drum or cone separator and deposit, and the gangue minerals with low density remain in the mainstream of the slurry and are discharged through different discharge ports to achieve the separation of gold and gangue. When processing a fine-grained carbonaceous gold ore, the centrifugal gravity separation method is used. Under the conditions of a drum speed of 3000-5000r/min and a feed concentration of 10%-20%, fine-grained gold can be effectively recovered, and the gold recovery rate reaches 50%-60%. The centrifugal gravity separation method has a good recovery effect on fine-grained gold, which can effectively overcome the problem of difficulty in gravity separation of fine-grained gold. The equipment is compact and occupies a small area. However, the equipment cost is high, the energy consumption is high, the requirements for equipment materials and manufacturing processes are high, and the operation and maintenance are complex.
The above is an introduction to the gold extraction technology of carbonaceous gold ore. The gravity separation method shows unique advantages in the treatment of carbonaceous gold ore by virtue of its characteristics of using mineral density differences for separation. In practical applications, the appropriate gravity separation process should be selected according to the specific characteristics of the ore, and combined with other mineral processing methods (such as flotation, cyanidation, etc.) for joint treatment to maximize the gold recovery rate and concentrate grade.