
15311826613
Click to add WeChatThe main component of fluorite is calcium fluoride, which is an important mineral raw material for obtaining fluorine. Generally, pure fluorite is colorless, while common fluorites are in various colors, such as light green to dark green, blue, green-blue, yellow, wine yellow, purple, violet, gray, brown, rose red, dark red, etc. These fluorite ores often contain other gangue ores or metal ores, such as calcite, mica, etc. So when fluorite contains mica calcite, how to dress it? Let's take a certain mica calcite type fluorite ore as an example to introduce its fluorite beneficiation method.

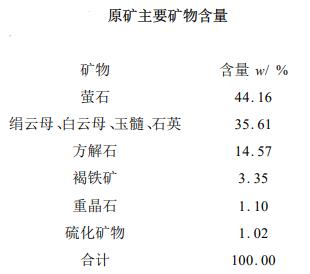
The types of ore contained in this mineral are: fluorite, calcite, sericite, muscovite, biotite, chalcedony, quartz, barite, limonite and trace amounts of pyrite, galena, sphalerite, chalcopyrite, etc.
Among them, fluorite is mostly semi-automorphic or heteromorphic polycrystalline granules or block aggregates in the ore. Due to the later fragmentation and dissolution, the fractures and dissolution holes of the fluorite aggregates are filled and replaced by carbonaceous calcite and scaly sericite, and chalcedony or limonite is filled and replaced locally. The fine dissolution holes arranged along the cleavage plane of fluorite are often filled with calcite or sericite. The coarse-grained fluorite is also impure, and other minerals with fine grains of 1 to 10 μm are encapsulated in it. These minerals form a complex and tight inlay with fluorite, and at the same time, fluorite contains impurity mineral inclusions that cannot be dissociated, so it is difficult to sort.
The carbonaceous calcite and scaly sericite in the mineral have the same floatability as fluorite. During roughing, most of the fluorite will enter the foam product with calcite and mica. If you want to effectively improve the recovery rate of fluorite, the flotation process needs to adopt a one-roughing and multiple (nine) fine process. The main reason is that when the intermediate ores from 1 to 4 are sequentially returned to the previous operation or concentratedly returned to the roughing operation, the flotation index of the fluorite concentrate is not ideal. Therefore, the intermediate ores from 1 to 4 are open-circuited, and the intermediate ores from 5 are also open-circuited. The intermediate ores from 6 to 9 are sequentially returned to the previous operation, which can not only improve the grade of the fluorite concentrate but also obtain a higher recovery rate.

Adopting the flotation process of one roughing and 9 fine cleaning, when the feed fineness is 97.48%-0.074mm, the feed contains 43.95% CaF2, 14.57% calcite, 35.61% mica, muscovite and chalcedony, a fluorite concentrate with a grade of 97.50% and a recovery rate of 80.97% can be obtained.
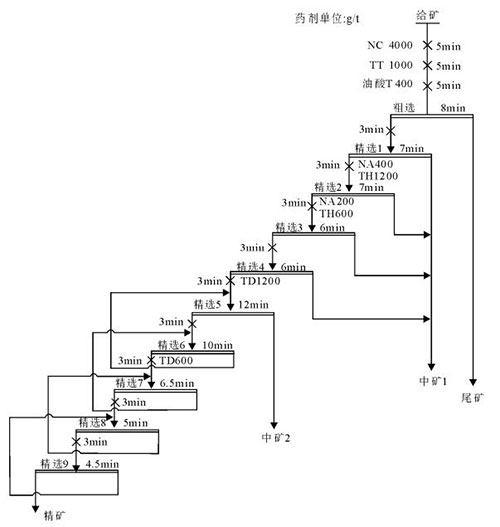
In the roughing section, oleic acid T is used as a collector, NC and TT are used as regulators, and the dosages are 4000g/t and 1000g/t respectively. The recovery rate of fluorite rough concentrate reaches 97%. In the 1st to 4th sections of the selection, NA and TH are used as regulators, and the dosages are 600g/t and 1800g/t respectively. Calcite can be effectively suppressed. In the 5th to 9th sections of the selection, TD is used as a regulator, and the dosage is 1800g/t. It can effectively suppress mica and further remove residual calcite and its intergrowths. While suppressing sericite, it can further remove residual calcite and its intergrowths.
The above is the beneficiation process of a mica-calcite fluorite ore. In actual beneficiation plants, since fluorite ores are mostly associated or paragenetic ores, and the properties of each fluorite mineral are different, it is necessary to determine the appropriate process plan according to the properties of the ore in order to effectively obtain a return on investment. Therefore, it is recommended to conduct a beneficiation test and design a suitable fluorite beneficiation process and fluorite beneficiation equipment through analysis.