
The gold mine heap leaching gold extraction process has simple process, low energy consumption, less equipment configuration, low infrastructure investment and production costs, and is widely used. It is mostly suitable for processing low-grade gold ores such as oxidized ores, by-product ores mined during tunnel development or off-surface ores.
Crushing, granulating, pretreatment, pad construction, pile building, leaching liquid preparation, liquid distribution and collection, rich liquid (rich liquid) processing

15311826613
Click to add WeChat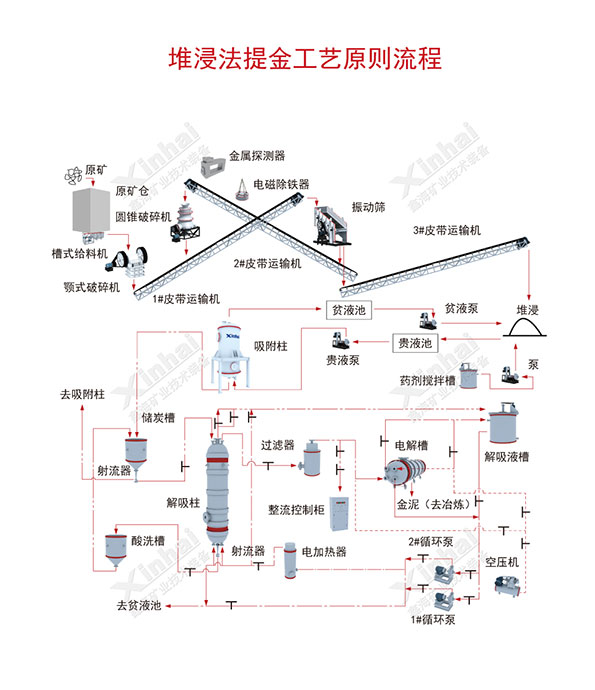
Gold ore is generally not crushed during heap leaching (accounting for 30%), the ore particle size after the second-stage crushing is 30-50mm (accounting for 53%), and the ore particle size after the third-stage crushing is 9-19mm (accounting for 17%).
For some mineral powders and gold ores with high clay content, granulation is required first. The process is: add a certain amount of ( 3-6kg/t) cement, lime adhesive, and add an appropriate amount of sodium cyanide solution to maintain the humidity of the ore at 8-12%, and solidify for 8-12 hours to form agglomerates.
During the granulation process, it is sometimes necessary to add leaching liquid to pretreat the ore. The purpose is to improve the permeability and The leaching rate of useful components in ores.
In order to collect the rich liquid and prevent the solution from leaking, the bottom of the pile must be trimmed and paved (or called bottoming) before building the pile. . The main materials for constructing dip pads include clay, sand, gravel, asphalt, reinforced concrete, plastic film or rubber plastic sheets. Depending on the material, the thickness of the cushion layer is generally 300-600mm. Vertical and transverse drain ditches are paved with lump ore on the cushion layer, and finally a layer of large ore is laid on the entire bottom plate to protect the bottom cushion.
The purpose of pile building is to make the pile have good and uniform permeability and ensure that the slope will not collapse. Generally, the pile height is 3-9m, and the raw ore heap leaching pile can be as high as 46m. There are many ways to build piles, including multi-pile method, multi-layer method, slope method, etc. Most gold mine heap leaching plants often use vehicles, front-end loaders, and bulldozers to transport and unload the ore to build piles, and at the same time loosen the piles in time to prevent the piles from being mechanically compacted.
Use water and leaching agent according to a certain formula to prepare a solution or leaching solution for leaching useful components from gold ore. Common leaching agents include sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, sodium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, ammonium carbonate, ammonium bicarbonate, iron sulfate, chloride, sodium iodide, potassium iodide, ammonium sulfate, air, oxygen, permanganate, Contains nitrogen oxides, hydrogen peroxide and chlorates, etc. The formula and dosage of the leaching solution need to be determined according to the mineral type, mineral composition and chemical composition. Alkaline sodium cyanide solution is often used as the leaching solution in gold mine heap leaching.
Liquid distribution is to spray the leaching liquid evenly on the top surface of the ore heap, and the liquid distribution pool, pump, and infusion pipe As well as spray pipes and sprinklers laid on the ore pile to form a liquid distribution system. During the spraying process, one is to spray the leaching solution evenly on the ore pile, and the other is to achieve the required spray intensity, that is, the amount of spray per unit area per unit time, usually 0.1-0.4L /m·min, the spray time accounts for about 1/3-1/2 of the total time. After spraying, the rich liquid from the bottom of the pile is collected into the liquid collection tank through the liquid ditch, and then pumped to the workshop for processing.
Use carbon adsorption and desorption electrolysis or zinc powder replacement precipitation to extract gold ore. Activated carbon becomes gold-loaded carbon by adsorbing gold in the slurry. After the adsorption operation is completed, the slurry containing gold-loaded carbon is sent to the carbon extraction screen through an air lifter to separate the slurry from the activated carbon. After screening and washing, the slurry is sent to desorption and electrolysis operations.